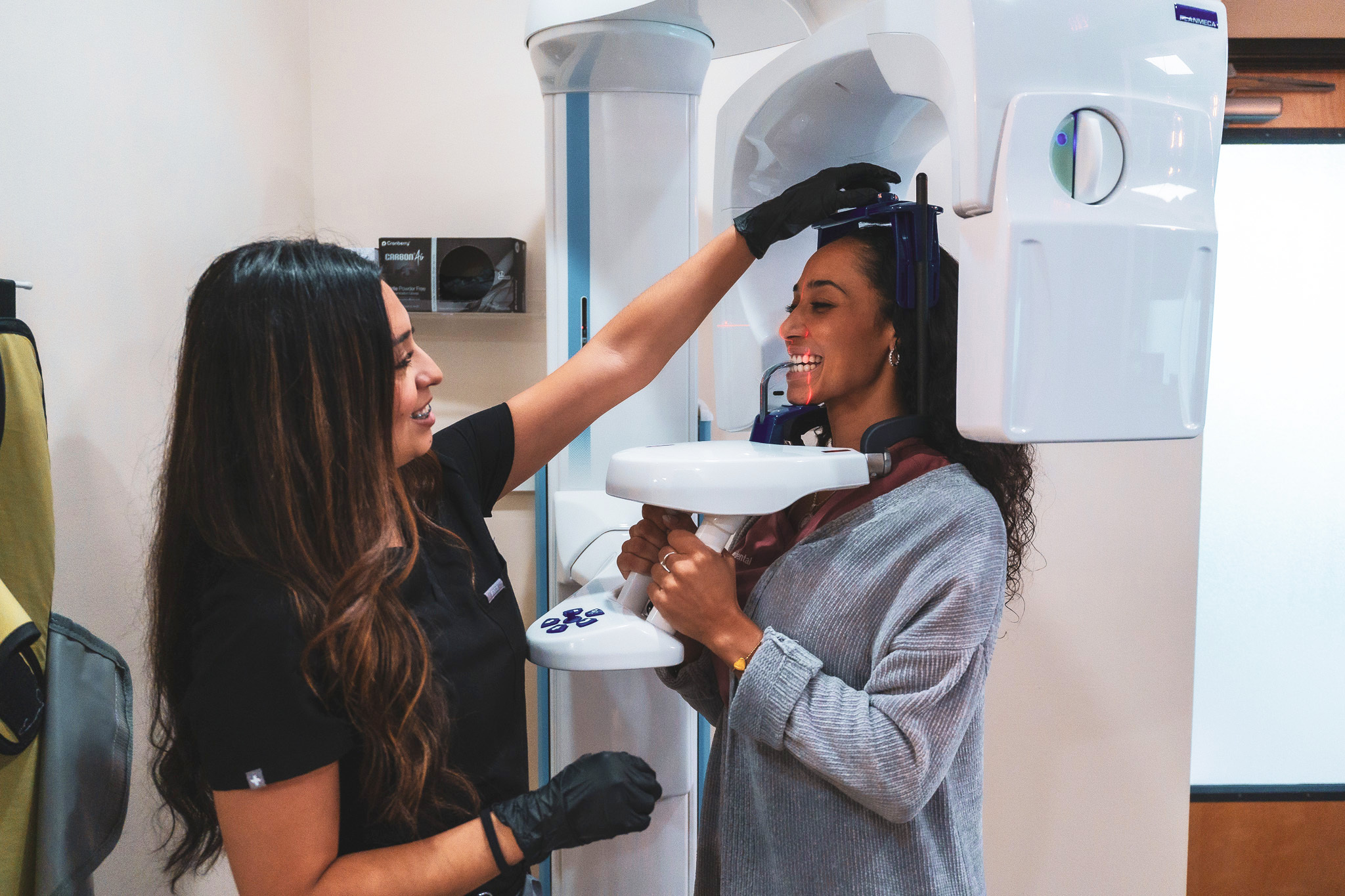
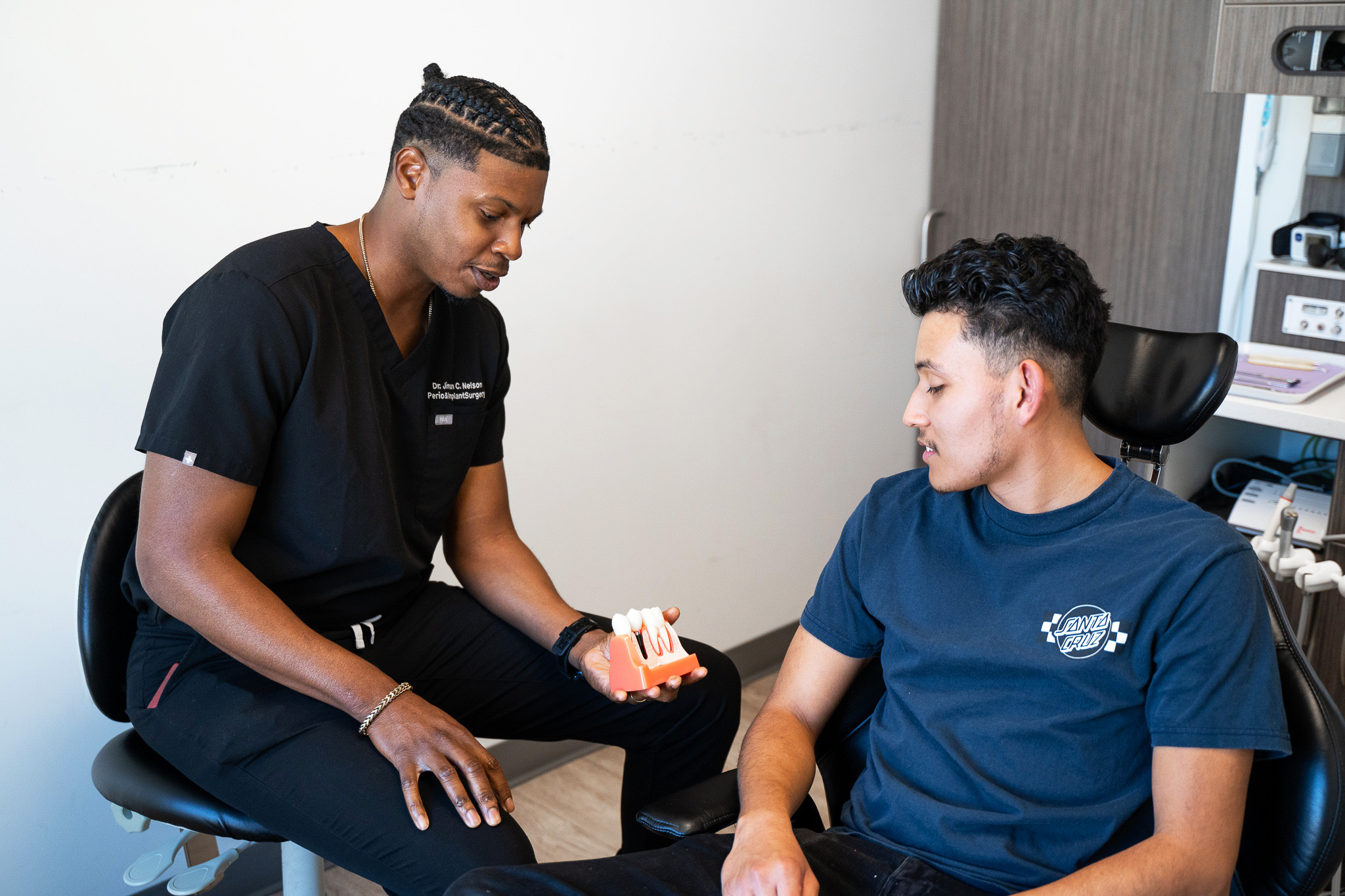
Missing teeth and tooth loss can lead to bone loss in the jaw. The jawbone does not only support your facial structure but also your teeth, which helps you to chew and speak properly. Thus the jawbone is an essential part of your face.
Bone atrophy in the jaw can be caused by several oral and medical conditions such as gum disease, tooth loss, bruxism, etc. If left untreated, this oral condition may affect other aspects of your oral and overall health and result in issues like distortion of the facial features, loosening of the remaining teeth, and a range of other concerns.
Tooth replacement procedure and dental bone grafts are the most common treatment for tooth loss bone loss. Are you concerned about potential tooth loss bone loss in your jaw? Consult your dentist right away. Your dentist office near me would recommend highly recommended bone loss treatment for you.
Signs and Symptoms of Dental Bone Loss
There is a high tendency that patients with either missing teeth or periodontal disease would experience bone loss in their jaw. Generally, bone loss is a gradual process and may not be noticed immediately. That is, the signs and symptoms of bone loss are not usually conspicuous. However, the most effective way to know if you have bone loss is to visit your dentist near me who will use cone beam imaging and x-rays to determine if you need bone loss treatment. Sometimes, some certain changes in your bite and facial features may indicate that you have bone loss. For instance, wrinkles may begin to form around the mouth, your chin may become more pointed, or your mouth may seem to collapse into your face. More so, you may experience bone loss with dentures. Patients with dentures often notice that their teeth may begin to shift forward in their mouth.What Causes Bone Loss in the Jaw?
Although the most common causes of bone loss are tooth loss and gum disease, there are other dental and medical issues that can lead to bone loss in your jaw. These include Smoking: Smoking can negatively affect the bone density in all areas of the body, including the jawbone. Missing Teeth: one of the functions of the teeth is to maintain the thickness and natural height of your jawbone. The presence of the teeth roots in the jaw stimulates the brain that resources are needed in a particular area of the jaw. As a result, the body sends the necessary nutrients to encourage bone growth in the jaw. However, in the case of missing teeth, there would be no stimulation to the brain and bone loss will occur instead of bone growth. The longer missing teeth are left untreated, the more bone tissue is lost, which can cause further tooth loss. Periodontal Disease: Periodontal disease affects the supporting structures of the tooth like the alveolar bone, bone tissue, supporting gum, and other ligaments. This causes tooth loss and bone loss in the jaw. Dentures and Dental Bridges: Traditional tooth replacement procedure includes dentures and dental bridges. These restoration methods can cheaply replace missing teeth to restore your natural smile and improve your ability to speak and eat naturally. However, dentures and dental bridges do not protect your jawbone against loss. In fact, there were reported cases of bone loss with dentures. Dental bridges are prosthetic teeth supported by dental crowns, which are placed over natural teeth. Since the jawbone beneath the supporting teeth is untouched and remains intact, the areas of the jawbone with the missing teeth will continue to lose bone tissue. Unlike with dental bridges, dentures can intensify loss of bone in the jaw. Traditional full dentures are not supported by the teeth or dental implants but rest directly on the gum tissues. Hence, dentures do not give enough stimulation to prevent bone tissue loss. Worse still, since dentures are not fixed, they tend to shift and rub against the gum tissue. This process can speed up bone loss in the jaw over time. Medical Conditions: Some certain medical conditions may also increase the likelihood of tooth loss bone loss in the jaw. These medical conditions include Osteoporosis, Paget’s disease of bone (PDB), Tumors, and Osteomyelitis. Accident and Trauma: Injury to the jawbone or trauma to teeth may also lead to bone loss. For instance, if a tooth is broken or knocked out, bone stimulation to the jaw will cease and this will lead to bone tissue deterioration. Additional causes of bone loss in the jaw include birth defects, infections, and certain prescription drugs.Treatment for Bone Loss in the Jaw
The most effective treatment for bone loss in the jaw is bone grafting. During the bone graft procedure, your dentist would replace the lost bone tissue with grafting material (usually from your own bone, donor bone, or synthetic grafting material). After a while, your body would absorb the grafting material, replace it with natural, healthy tissue, and restore the volume and emergency dentist of your jawbone. Also, recent studies on alternative treatments for jawbone loss revealed that osteoporosis can be treated with a drug known as Teriparatide. However, studies into Teriparatide are still ongoing.How to Prevent Bone Loss in the Jaw
Avoiding smoking will prevent the deterioration of the jawbone tissues, which will subsequently prevent bone loss in the jaw. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes brushing and flossing at least twice daily, avoiding bruxism and shock to the teeth, etc., can help to prevent jawbone loss and protect the overall health of your jaw. Like stated above, missing teeth can lead to bone loss in the jaw and the longer missing teeth are left untreated, the more bone tissue is lost. And the method of tooth replacement procedure also matters in preventing bone loss since the traditional tooth replacement procedures, such as denture and dental bridges, would not prevent bone loss. However, a tooth replacement procedure viable to help prevent your jawbone from deteriorating is tooth implant. Tooth Implants: Tooth implants, also known as dental implants, are the most effective tooth replacement procedure. Tooth implants are small titanium posts that function as natural tooth roots and provide necessary supports for the dental crown and needed stimulation to your jawbone. Since the dental implants stimulate the surrounding tissue and the brain just like the natural teeth roots, they encourage the body to send necessary nutrients to trigger bone growth in the jaw. However, you can experience tooth implant bone loss if undergo tooth extraction but do not qualify for immediate placement of a tooth implant. To prevent tooth implant bone loss, undergoing a socket preservation grafting can help prevent bone tissue loss in the area. Finally, just like any other bone in your body, your jawbone requires some certain nutrients, such as calcium, phosphorus, protein, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients. Therefore, eating plenty of vegetables, whole fruits, and a well-balanced diet can help to increase your bone health. If you need more information on the causes and prevention of bone loss, don’t hesitate to contest us.URBN Dental Services in Houston, TX
Houston | Katy | Montrose | West University Place | Greater Third Ward | Greater East End | North East Houston | Houston Heights | Central Northwest | Fairbanks | Acres Home | East Houston | Southeast Houston | Central Southwest | Fort Bend Houston | Brays Oaks | Meyerland Area | Sharpstown | Alief | Westchase | Memorial | Northwest Houston | Katyland | Whispering Lakes | Pine Lakes | Woodcreek Reserve